PERFECT TENSES:
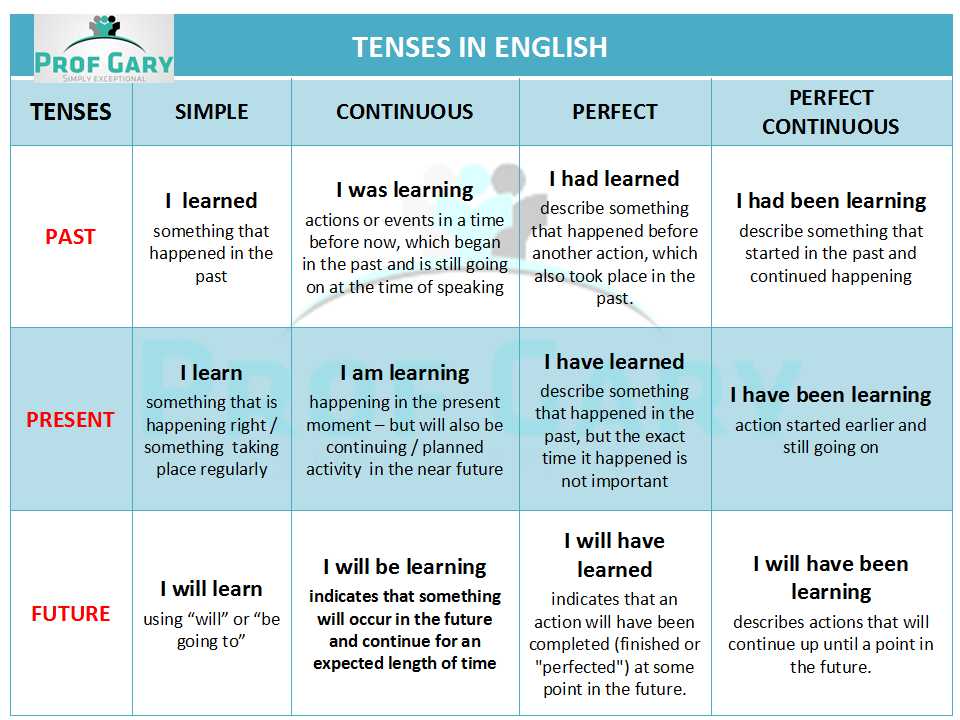
The Present perfect can be used to describe an action that starts in the past and finishes in the present. Formed with have/has + past participle.
The Past perfect describes an action that started in the past and finished in another point in the past. Formed with had + past participle.
The Future perfect describes an action that started in the present, past or future that ends in a more distant future. Formed with will have + past participle.
CONTINUOUS tenses:
The Present continuous can be used to show an action which is happening at the time of speaking. I am having dinner at the moment.
***
The Past continuous can be used to show an action which was happening in the past. It is important to remember that the Past continuous is usually used to show an action which was happening when another action, which is usually shorter, happened at the same time, stopped the continuous action or started after the continuous action.
I was having dinner when Sarah called me.
I was walking along the beach when it started raining. The
***
Future continuous is used to show that an action will be happening at a time in the future. I will be having dinner at my parents’ house tomorrow.
PERFECT CONTINUOuS (PROGRESSIVE):
Perfect means “complete,” and Continuous / Progressive means “unfinished.”
Perfect progressive sentences focus on the completion of an action that is, was or will be in progress.
Present Perfect continuous
You form the present perfect progressive by using have been (or has been) followed by an –ing verb.
For instance, “She has been sitting in class since early this morning.” The action,sitting, is continuing. But the emphasis is on the completed part of the action. Here are some more examples:
I have been waiting for 20 minutes.
I have been studying since I was a child.
It has been snowing all day long.
***
Past Perfect continuous
The past perfect progressive emphasizes the duration of a past action before another action happened.
For example, “I had been smoking for 10 years before I quit.”
You form the past perfect progressive by using had been followed by an –ing verb.
Notice how the past perfect progressive often includes the adverbs for and since to express duration. You will also see the adverbs before, when or by the time used to introduce a second action.
The second action uses the simple past tense. Here are some more examples:
I had been studying for 12 years by the time I graduated from high school.
She had been living there since she was a child.
He had been teaching for 12 years before he was certified.
***
Future Perfect continuous
The future perfect progressive describes the duration of an action as it relates to a future event.
There are two ways to form the future perfect progressive. Both require two actions.
One is by using “will have been” plus a present participle, followed by “when” or “by the time” and the second action.
For example, “I will have been working for 35 years by the time I retire.” Notice that the second planned action, retire, is in the simple present. The simple future is never used with the second action.
The other way to form the future perfect progressive is using “be going to have been” plus a present participle followed by “when” or “by the time” and the second action. The order of the actions can be reversed with either form.
For example, “By the time the plane arrives, I am going to have been waiting for five hours.”
With the future perfect progressive, it is not always clear if the –ing verb started in the past or will start in the future. For example, “The doctor will have been working for 24 hours by the time his shift is finished.”
The future perfect progressive is rare because it is difficult to know the duration of an activity relative to another future event.
And those are the three perfect progressive tenses in English.
We have been talking about verb tenses for several weeks now. It is time to move on to other topics. We leave you with a present perfect progressive song by the music band “Foreigner.”
“I’ve been waiting for a girl like you to come into my life”